Surging shipping rates pose new headwind for the global economy
Shocks to supply chains are engulfing a wider swath of the global economy as the pandemic rages on, threatening to stifle Asia’s trade-led recovery just as soaring freight rates make it harder for businesses to weather another year like 2020.
Shortages of consumer goods like paper towels and work-from-home gear early in the Covid-19 crisis have given way to parts shortfalls in one of the most globally integrated of industries: auto manufacturing.
Volkswagen AG was forced cut production plans at the world’s largest car factory in Germany and warned supply constraints might spread globally, while Honda Motor Co. is reducing output at five North American factories as it struggles to procure chips used to make cars.
“The supply-side bottlenecks seem to be more pronounced in the U.S. and Europe where supply delivery times are slowing again,” said Rob Subbaraman, global head of macro research at Nomura Holdings Inc. in Singapore. “This is negative for industrial production in the west and should result in a sharper drawdown in inventories and upward pressure on output prices.”
Compounding the industrial imbalances are transport woes plaguing consumer and health-care sectors still dealing with a dearth of available shipping containers to move components and finished products out of China, Taiwan, South Korea and Asia’s other export powers.
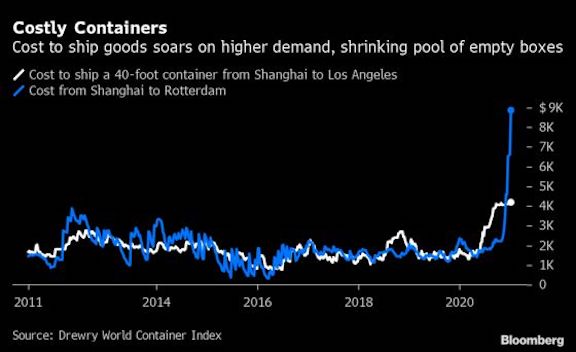
Nerijus Poskus, vice president for global ocean at San Francisco-based freight forwarder Flexport Inc., reckons the world needs the equivalent of 500,000 more 20-foot containers—roughly enough to fill 25 of the largest ships in operation—to satisfy the current demand. In the meantime, standard container rates on transpacific routes are quadruple what they were a year ago. And that’s before equipment surcharges and premiums for guaranteed loading are added.
“Anyone paying the freight bills in 2020 though knows the true cost of shipping is much higher than even the recently increased rates,” Poskus said. “We expect that to only increase in 2021.”
Just a few weeks ago, the bottlenecks at ports from Singapore to Los Angeles and Rotterdam were looking like short-term headaches and added costs during peak season. Now they’re threatening to act more like a brake on the global recovery.
Crimping Demand
That’s because the convulsions are reaching beyond supply chains into operations, either curbing output or saddling manufacturers with goods that haven’t been paid for, and wreaking havoc on inventories and cash flows. In some cases, supply snarls are begetting demand drags: Some factories complain they can’t consider new orders until the clogged pipeline clears.
Satellite tracking shows almost three dozen container ships are anchored waiting for berth space at the twin ports near L.A., the busiest gateway for U.S. goods trade, up from about 20 vessels right before Christmas.
Among those feeling the pain is Sidney Yu, whose firm Prime Success Enterprises Ltd. makes educational and recreational products that includes tents for children and baths for pets. After booking two containers to Europe for a shipment last month from Yantian, Shenzhen, he was later told he could only get one.
“When we went to the container terminal to take the container they said ‘sorry, there’s no container anymore, they are all used up,’” said Yu, director of the Hong Kong-based company, which has manufacturing facilities in Guangdong. “Things like this are happening which we have never experienced before.”
Containers that once would have cost $2,000 to send across the Pacific are now being quoted as high as $13,000 for service before Chinese New Year in mid-February, he said.
While most shipping analysts see the congestion lasting through the first quarter, there may be longer-term economic costs—both for consumers to bear or companies’ margins as higher transport costs get baked into annual contracts with container carriers.
“We know that the freight pressure across retail is here to stay and we’ve built that into our future plans,” Mark Tritton, the chief executive of Bed Bath & Beyond Inc., said last week on a conference call.
Supply Uncertainties
The outlook gets no less murky heading into February—when Chinese New Year marks a seasonal turn in Asian exports, many importers renegotiate freight rates with carriers for the next 12 months and the carriers themselves start to receive tens of thousands of new containers they ordered last year.
Elevated container rates “may factor in for the rest of the year,” even if the current disruptions get ironed out, said Chris Rogers, lead trade analyst for S&P Global Market Intelligence’s Panjiva. “Companies that have seen much higher shipping costs are either going to have to swallow that in their profits or pass it through to their customers.”
Normally container rates drop 15% to 20% after the Chinese holiday, he said, but “that might not happen exactly the same this year because the backlog has got to be cleared.”
There’s a lot riding on manufacturing to drive the global economic recovery given the doldrums that tourism and hospitality are mired in. The World Bank this month warned that the rebound from the deepest recession since World War II will be slightly weaker than previously expected.
The Washington-based lender also trimmed its global trade volume growth forecast to 5% in 2021 following a 9.5% contraction last year.
Still, there are good reasons for optimism. China won a record share of world trade last year and Taiwan’s exports continued their double-digit recovery in the final month of 2020.
Meanwhile, South Korea’s exports climbed at the fastest pace in more than two years in December. The country’s biggest shipping line HMM Co. has deployed extra ships along U.S.-bound routes and will add another ship to Europe later this month.
The extra capacity is needed to help small companies on the receiving end. The European Freight Forwarders Association and the European Shippers’ Council sent a letter to regulators in Brussels this month warning of business failures if the shipping market doesn’t rebalance.
In Asia, the situation is unprecedented for Kenway Lam, who runs a Hong Kong-based maker of packaging machinery. Last month he was all set to ship to a customer in Uruguay who had agreed to the deal months earlier.
At the last minute, Lam was told no containers were available.
“It’s like getting a concert ticket but you cannot book it, you cannot purchase it online,” said Lam, managing director of Kizui Packaging Machinery Co., whose manufacturing is completed in Guangdong and Taiwan. “Once it is available, there will suddenly be a price and either you take it or the container will be gone.”
Similar Stories

ZIM launches its USA Employer Brand Campaign to attract top talent
View Article
Hapag-Lloyd achieves good result in first three quarters of 2024
View Article
Decoding alternative fuels: OceanScore supports tricky bunker selection process under FuelEU Maritime
View Article
Wallenius Marine’s new vessel “Way Forward” ready for her first mission
View Article
Dedicated safety advocate celebrates 40-year career
View Article
Potential implications on the freight industry following 2024 U.S election / Signal Ocean
View ArticleGet the most up-to-date trending news!
SubscribeIndustry updates and weekly newsletter direct to your inbox!





